From electricity to green gas
Power-to-gas technology exploits the phenomenon of electrolysis: excess energy from wind farms, photovoltaic fields and electrical infrastructure congestion is used to break the bonds of the water molecules and produce hydrogen.
Green hydrogen can be upgraded on site where there is consumption, for example in the automotive sector, or transported to the point of use via new dedicated infrastructure or, alternatively, using the existing gas network (up to permitted compatibility percentages).
This infrastructure is evolving so as to be able to accept increasing quantities of hydrogen that can be injected into the grid thanks to the use of blending systems. This is a technological constraint that can now be completely overcome thanks to power-to-methane (P2M) solutions.
In fact, we can convert hydrogen produced from electric energy into methane and water by making use of the Sabatier reaction by using an external source of carbon dioxide. This methanation process, which can take place via biological or catalytic routes, produces a valuable energy vector that has the same characteristics as traditional natural gas and can therefore be transported and stored in a similar manner.
If the carbon dioxide used is renewable in origin (biogas, biological fermentation processes, etc.), the green molecules obtained via methanation are considered to be biomethane.
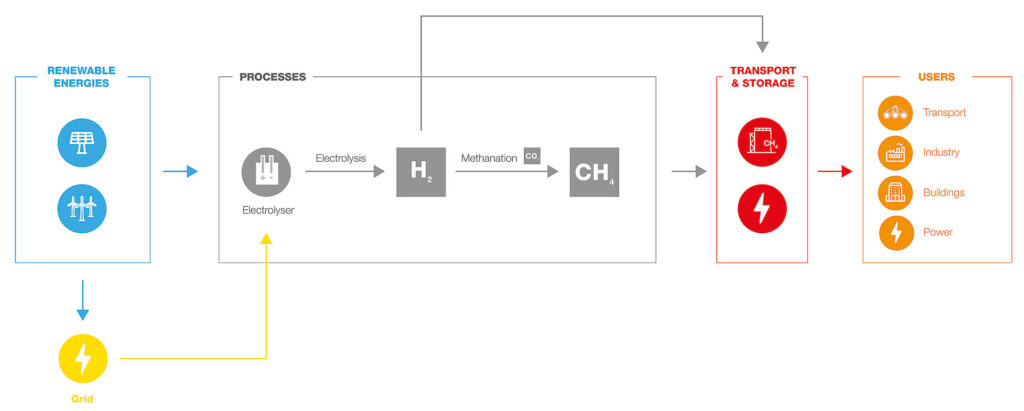
Storage of renewable energy using Power-to-gas technology

