BIOGAS VS BIOMETHANE
FROM BIOGAS TO BIOMETHANE

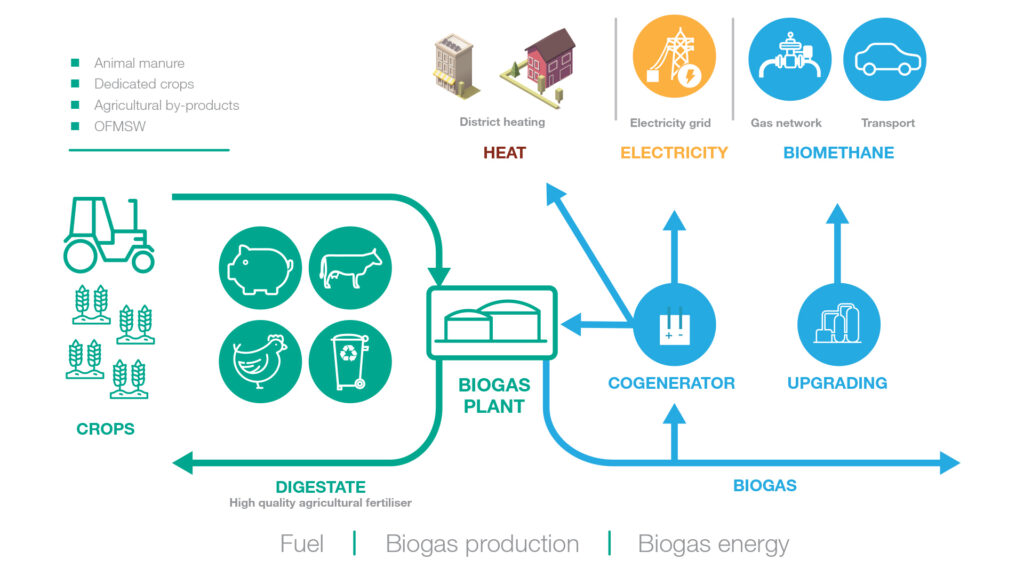
Biogas is mostly made up of methane (between 50-70%) and is produced by the digestion of organic waste from agricultural biomass (dedicated crops, by-products, agricultural waste and animal manure), agro-industrial biomass (waste from the food processing chain), industrial processing waste, municipal wastewater sludge and organic fractions of municipal solid waste (OFMSW).
Biomethane is a biogas that has undergone a refining process to get a concentration of methane equal to or greater than 97%, which can be used in the same way as natural gas by being injected into the network or as biofuel in gaseous or liquefied form for transportation.
HOW TO MAKE BIOMETHANE
The conversion from biogas to biomethane occurs through a process of upgrading, which removes carbon dioxide through a multi-step molecular separation process. The various stages of the process (pre-treatment, dehydration, compression, etc.) are optimised depending on the upgrading technology chosen and the composition of the biogas to be treated.
In addition to carbon dioxide, other gases are also removed, such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, siloxanes, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contaminants and other inert substances present within the biogas. It is essential to remove these substances because, if they remain present, they could give rise to different problems: they could end up being released into the atmosphere, or they could remain in the biomethane and alter its quality specifications, as well as affect the proper operation of the plant itself. In addition, the presence of VOCs leads to negative effects on the odorability of biomethane.
WHAT HAPPENS AFTER BIOGAS UPGRADING
Biomethane obtained after the upgrading phase is eligible to undergo the various stages of controls over the quality, metering, compression, regulation and possible odorisation. These stages must necessarily be completed before one of the possible next stages:
- Network injection stage – it could be transport or distribution network – to be executed in compliance with the specifications laid down by the applicable legislation. This stage requires dedicated solutions.
- Production of liquefied biomethane (LNG), which requires dedicated quality analysis and fiscal metering solutions.